Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) in Manufacturing: Differences You Need to Know
High QA
April 28, 2022
An organization must be aware of the differences and definitions of Quality Control (QC) and Quality Assurance (QA).
Both are essential components of an organization’s quality management strategy, and the success of quality processes are contingent upon all stakeholders, including management and all employees comprehending the distinctions.
An effective quality process can significantly contribute to the success of a project. Still, when they are misunderstood, they are likely to be useless in ensuring that the manufactured part is delivered on time, built within the team’s budget, and meets the customer’s needs.

What is Quality Control (QC)?
Quality Control, usually abbreviated as QC, is concerned with identifying defects. QC verifies that the part is manufactured within the design standards and ensures that deliverables adhere to stated quality requirements.
Quality Control is a reactionary process that is based on detection. It is used to identify flaws in a manufactured part.
What is Quality Assurance (QA)?
Quality Assurance is abbreviated as QA and is concerned with fault prevention. Quality Assurance guarantees that the projects’ approaches, techniques, methodologies, and processes are implemented correctly.
Quality assurance activities check and verify that the processes for managing and creating deliverables are being followed and are functioning correctly.
QA is a proactive procedure that is geared toward prevention. It identifies process weaknesses and areas for improvements.

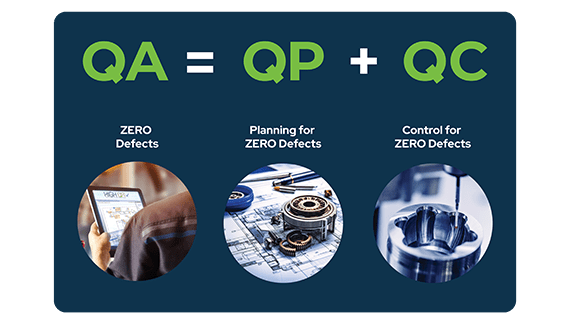
Quality Assurance (QA) or Quality Control (QC)
To fully comprehend the distinctions between quality assurance and quality control, you must first understand how the two processes interact to improve your organization’s quality and eliminate corrective actions.
1. Dedicated Personnel in QC vs Entire Team in QA
The entire staff participates in quality assurance operations. QC on the other hand has a select department or group of individuals responsible for finding flaws. QA activities are the responsibility of every participant in the manufacturing facility.
QA operations include defining processes, team training, and educated tool selection. Auditing is also a part of quality assurance.
2. Process-oriented in QA vs Product-oriented in QC
Quality assurance is a process-oriented discipline that focuses on preventing quality problems. QC focuses on discovering quality concerns in manufactured products that may affect consumer satisfaction. Actions vs results is another way to think about this dichotomy. QA is concerned with the processes, whereas QC is concerned with the finished product.
3. QA is Proactive while QC is Reactive
Quality assurance that works is proactive. Its goal is to use processes to prevent problems from occurring in the first place. QC is a reactive process that seeks to find faults in product quality after a part is made.
Every time you follow the quality process, the result should be a safe, effective product. Testing items to ensure that they fulfill safety and efficacy criteria is known as quality control. If you discover quality issues during QC testing, you should take immediate action to prevent a dangerous product from being transported and disseminated.
In an ideal world, QC concerns would also prompt a QA audit. Non-conforming test findings should trigger a corrective and preventative action study to uncover the root cause of quality issues and improve manufacturing and quality processes to avoid recurrence.
4. Quality Assurance is based on Process, while QC concentrates on Verification
QA efforts produce a plan for developing high-quality goods. Some aspects of quality assurance are standardized in the ISO 9000. In addition to these standards, manufacturers should further develop and employ their own internal standardization practices.
QC entails checking products after they’ve been manufactured and before they’re distributed and ensuring their safety and efficacy.
QC is usually the part of an organization whose responsibilities include following standard operating procedures for product testing. Quality control personnel follow standard operating procedures (SOPs) and document their findings using standardized product testing and process validation techniques.
The Benefits of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance provides multiple benefits to manufacturers who make QA a priority.
Increased Cost Savings
As a proactive component of quality management, good QA leads to the prevention of quality issues. There are fewer scrap parts and material, returned products and recalls.
Increased Production Efficiencies
With fewer defective products, manufacturers can allot resources such as time and money to additional projects. It takes fewer resources to produce quality goods if processes are in place that support quality manufacturing.

Increased Customer Satisfaction
When manufacturers employ effective quality assurance techniques, customers receive better products on faster timelines and with greater levels of consistency. With a lower likelihood of receiving a defective product, customers can also see benefits further down the line for additional projects with greater personalization and innovation. This equates to greater customer retention and increased revenue.
Using High QA for Quality Assurance
Maintaining quality is a constant challenge for manufacturers. Using information from quality control, manufacturers can implement corrective quality assurance processes to make parts on specifications, on time and on budget.
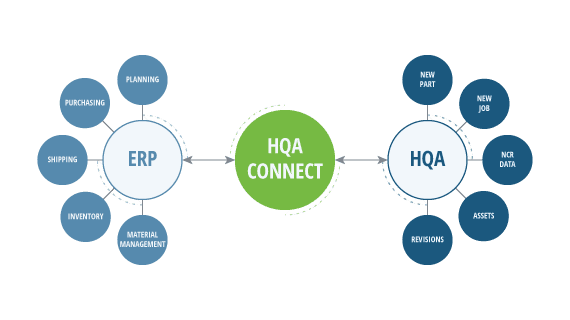
High QA provides the ideal solution for both quality control and quality assurance. As a single source of truth for quality within your organization all authorized employees can securely access QA and QC processes and data and use that information to generate all the necessary FAI, PPAP and submission package documents.

Our manufacturing quality management solution (QMS) software will help you save 75% of your time. Take your manufacturing from good-to-great with an all-in-one quality software solution.
Explore our website and discover what High QA can do for you and your suppliers. We are just a click away to answer questions or provide a demo of our software.
For more information, visit www.HighQA.com or contact a High QA representative for a free no-obligation demo of Inspection Manager, the ultimate manufacturing quality management software.